The Church of North India (CNI) is the dominant united Protestant church in northern India. It was established on 29 November 1970 by bringing together the Protestant churches working in northern India. It is a province of the worldwide Anglican Communion and a member of the World Methodist Council and the World Communion of Reformed Churches. The merger, which had been in discussions since 1929, came eventually between the Church of India, Pakistan, Burma and Ceylon (Anglican), the United Church of Northern India, (Congregationalist and Presbyterian), the Methodist Church, Disciples of Christ denominations.
The CNI’s jurisdiction covers all states of India with the exception of the five states in the south (Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu which are under the jurisdiction of the Church of South India) and has approximately 2,200,000 members (0.1% of India’s population) in 3,000 pastorates.
History
| Part of a series on |
| Christianity in India |
|---|
 |
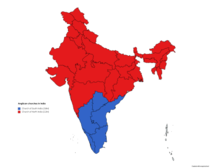
Church of North India in red and Church of South India in blue
Ecumenical discussions with a view to a unified church were initiated by the Australian Churches of Christ Mission, the Methodist Church of Australia, the Wesleyan Methodist Church, the Methodist Episcopal Church and the United Church of Northern India during a round table meeting in Lucknow in 1929.
A negotiation committee was set up in 1951 using the plan of Church Union that resulted from the earlier consultations as its basis. The committee was composed of representatives from the Baptist Churches in Northern India, the Church of India, Pakistan, Burma and Ceylon, the Methodist Church (British and Australian conferences), the Methodist Church in Southern Asia and the United Church of Northern India (UCNI). The Methodist Episcopal Church, however, did not join the discussions and, in 1981, it became the Methodist Church in India (MCI). In 1957, the Church of the Brethren in India and the Disciples of Christ denominations joined in the negotiations as well.
A new negotiation committee was set up in 1961 with representatives from all the above-mentioned denominations. In 1965, a finalized plan of Church Union, known as the 4th Plan of Union 1965, was made. The union was formalized on 29 November 1970 when all the negotiating churches were united as the Church of North India with the exception of the Methodist Church in Southern Asia, which decided not to join the union.
Beliefs and practices
The CNI is a trinitarian church that draws from the traditions and heritage of its constituent denominations. The basic creeds of the CNI are the Apostles’ Creed and the Nicene Creed of 381 AD.
Liturgy
The liturgy of the CNI is of particular interest, as it combines many traditions, including that of the Methodists and such smaller churches as the Church of the Brethren and the Disciples of Christ. Provision is given for diverse liturgical practices and understandings of the divine revelation.
Governance
The polity of the CNI brings together the episcopal, the presbyterial and the congregational elements in an effort to reflect the polity of the churches which entered into union. The episcopacy of the CNI is both historical as well as constitutional. There are 26 dioceses, each under the supervision of a bishop. The main administrative and legislative body is the synod, which meets once every three years to elect a presiding bishop, called a moderator, and an executive committee. The moderator acts as the head of the church for a fixed term; another bishop is elected Deputy Moderator.
Social involvement
Social involvement is a major emphasis in the CNI. There are synodal boards in charge of various ministries: Secondary, Higher, Technical and Theological Education, Health Services, Social Services, Rural Development, Literature and Media. There is also a synodal Programme Office which seeks to protect and promote peace, justice, harmony and dignity of life.
The CNI currently operates 65 hospitals, nine nursing schools, 250 educational institutions and three technical schools. Some of the oldest and well-respected educational institutions in India like Scottish Church College in Calcutta, La Martiniere Calcutta, Wilson College in Mumbai, St. James’ School, Calcutta, Hislop College in Nagpur, St. John’s Diocesan Girls’ School, Calcutta, St. Paul’s School in Darjeeling, St. John’s College in Agra and College Bishop Cotton School in Shimla, Christ Church College, Kanpur, Sherwood College, Nainital, Ewing Christian College, Prayagraj, Boys High School, St. Andrew’s College in Gorakhpur are under the administration of the CNI.
Ecumenism
The CNI participates in many ecumenical bodies as a reflection of its commitment towards church unity. Domestically it participates in a joint council with the Church of South India and the Mar Thoma Syrian Church known as the Communion of Churches in India. It is also a member of the National Council of Churches in India. Regionally, the CNI participates in the Christian Conference of Asia and on an international level it is a member of the World Council of Churches, the Council for World Mission, World Alliance of Reformed Churches, World Methodist Council and in full communion with the Anglican Communion. The CNI is also in partnership with many other domestic, regional and international Christian agencies.
Gallery
-

St. Paul’s Cathedral, Kolkata
-

All Saints Cathedral, Prayagraj
-

Cathedral Church of the Redemption, New Delhi
-

Christ Church, Shimla
-

St. John’s Church, Meerut
-

St. James’ Church, New Delhi
-

St. Thomas’ Cathedral, Mumbai
-

The Wilson College, Mumbai
-

La Martiniere College, Lucknow
-

La Martiniere College, Calcutta
-
Present administrators
- Moderator: Rt. Rev. Bijay K. Nayak, Bishop of Phulbani
- Deputy moderator: Rt. Rev. Paul B.P. Duphare, Bishop of Nagpur
- General secretary: Rt. Rev. Pradip K. Samantroy, Bishop of Amritsar and former Moderator- Interim charge
- Honorary treasurer: Prem Masih
As of December 2022.
Moderators
Since its formation in 1970, the Synod of the CNI has elected a Moderator and one Deputy every three years.
Term Moderator Deputy Moderator April 1971 – July 1974 Eric Nasir,
Bishop in Delhi (and Rajasthan)Ramchandra Bhandare,
Bishop in NagpurJuly 1974 – October 1977 October 1977 – October 1980 October 1980 – November 1983 Ramchandra Bhandare,
Bishop in NagpurDinesh Chandra Gorai,
Bishop in CalcuttaNovember 1983 – October 1986 Dinesh Chandra Gorai,
Bishop in CalcuttaDin Dayal,
Bishop in LucknowOctober 1986 – October 1989 Din Dayal,
Bishop in LucknowJohn Ghosh,
Bishop in DarjeelingOctober 1989 – October 1992 John Ghosh,
Bishop in DarjeelingFranklin Jonathan,
Bishop in JabalpurOctober 1992 – October 1995 Anand Chandu Lal,
Bishop in AmritsarDhirendra Mohanty,
Bishop in CuttackOctober 1995 – October 1998 Dhirendra Mohanty,
Bishop in CuttackVinod Peter,
Bishop in NagpurOctober 1998 – January 2001 Vinod Peter,
Bishop in Nagpur
(died December 2000)James Terom,
Bishop in ChotanagpurJanuary – October 2001 James Terom,
Bishop in ChotanagpurBrojen Malakar,
Bishop in BarrackporeOctober 2001 – October 2004 James Terom,
Bishop in ChotanagpurJoel Mal,
Bishop in ChandigarhOctober 2004 – October 2005 October 2005 – October 2008 Joel Mal,
Bishop in ChandigarhPurely Lyngdoh,
Bishop in North East IndiaOctober 2008 – October 2011 Purely Lyngdoh,
Bishop in North East IndiaPhilip Marandih,
Bishop in PatnaOctober 2011 – October 2014 Philip Marandih,
Bishop in PatnaPradeep Samantaroy,
Bishop in AmritsarOctober 2014 – 3 October 2017 Pradeep Samantaroy,
Bishop in AmritsarPrem Singh,
Bishop in JabalpurOctober 2017 – 23 August 2019 Prem Singh,
Bishop in JabalpurProbal Dutta,
Bishop in Durgapur and Kolkata23 August 2019 – 14 September 2022 Bijay Nayak,
Bishop in Phulbani15 September 2022 – present Bijay Nayak Paul B.P. Duphare Dioceses
Diocese of Calcutta
When originally founded in 1813, the fourth overseas diocese of the Church of England covered all the subcontinent, all Australasia and some of Africa. With its 1835 split to create Madras diocese, Calcutta was made metropolitan over all its original area, and has been split many times since. The Bishop of Calcutta remained Metropolitan of India until the CNI’s 1970 creation; the current diocese covers parts of Bengal and the bishop is Paritosh Canning.
Diocese of Mumbai
Split from Calcutta diocese in 1837,[11] the Diocese of Bombay was the last new Indian diocese of the Church of England before all colonial dioceses became independent in 1863. Like Calcutta, Mumbai diocese has been a very large Church of England diocese, a diocese of the independent Indian Anglican church, and now a United Church diocese. The CNI diocese today covers Maharashtra, and the bishop is Prakash D. Patole.
Diocese of Chotanagpur
Founded from Calcutta diocese in 1890, the current diocese is based in Ranchi, its territory is Jharkhand and the bishop is B. B. Baskey.
Diocese of Lucknow
Erected in 1893 from the Diocese of Calcutta. The diocese is headquartered at Allahabad and serves Uttar Pradesh.
Diocese of Nagpur
The diocese was originally created in 1902/03, from Chotanagpur diocese.
Diocese of North East India
The CNI Northeast diocese, based in Shillong, North East India is headed by bishop Michael Herenz.[16] It originated as the Diocese of Assam, in the Anglican Church of India, erected from Calcutta in 1915;[17] and became known by the present name before 1986.
Diocese of Nasik
In 1929, Nasik diocese was founded from Bombay; her present bishop is Sharad Gaikwad.
Name Founded Headquarters Location Bishop Website Diocese of Delhi 1947, from Lahore New Delhi Delhi, Haryana Paul Swarup Diocese of Amritsar 1953, from Lahore Amritsar Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir P. K. Samantaroy www.amritsardiocesecni.org Diocese of Barrackpore 1956, from Calcutta Barrackpore West Bengal Paritosh Canning Diocese of Andaman and Nicobar 1966, from Calcutta Port Blair Andaman and Nicobar Islands Christopher Paul Diocese of Jabalpur 1970, from Nagpur Jabalpur Madhya Pradesh Vacant http://dioceseofjabalpur-cni.org/ Diocese of Patna bef. 70 Bhagalpur Bihar and Jharkhand Philip P. Marandih Diocese of Cuttack 1970 Cuttack Cuttack, Odisha Surendra Kumar Nanda http://www.dioceseofcuttackcni.in/ Diocese of Bhopal betw. 70-79, from Jabalpur Indore Madhya Pradesh Manoj Charan Diocese of Rajasthan 1981, from Delhi Ajmer Rajasthan Darbara Sing Diocese of Gujarat betw. 70-96 Ahmedabad Gujarat Silvans Christia Diocese of Kolhapur betw. 70-96 Kolhapur Maharashtra Sandeep Suresh Vibhute Diocese of Durgapur betw. 70-96 Durgapur West Bengal Sameer Issac Khimla Diocese of Chandigarh 1974, from Amritsar Ludhiana Chandigarh, Punjab Denzel Peoples Diocese of Agra 1976, from Lucknow[33] Agra Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand Prem Prakash Habil http://cnidioceseofagra.org Diocese of Eastern Himalaya bef. 1987 — Darjeeling, renamed c. 1992, from Barrackpur Darjeeling West Bengal, Bhutan, parts of Assam vacant
Acting: Michael HerenzDiocese of Sambalpur bef 96 Bolangir Odisha Pinuel Dip Diocese of Phulbani 1997, from Cuttack Kandhmal Odisha Bijay K. Nayak Diocese of Marathwada c. 2000 Aurangabad Maharashtra M. U. Kasab[ Diocese of Pune c. 2000 Pune Maharashtra Andrew Rathod Diocese of Chhattisgarh 2010, from Jabalpur Raipur Chhattisgarh Ajay Umesh James
