Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease has since spread worldwide, leading to an ongoing pandemic.
Symptoms of COVID‑19 are variable, but often include fever, cough, headache, fatigue, breathing difficulties, and loss of smell and taste. Symptoms may begin one to fourteen days after exposure to the virus. At least a third of people who are infected do not develop noticeable symptoms. Of those people who develop symptoms noticeable enough to be classed as patients, most (81%) develop mild to moderate symptoms (up to mild pneumonia), while 14% develop severe symptoms (dyspnea, hypoxia, or more than 50% lung involvement on imaging), and 5% suffer critical symptoms (respiratory failure, shock, or multiorgan dysfunction). Older people are at a higher risk of developing severe symptoms. Some people continue to experience a range of effects (long COVID) for months after recovery, and damage to organs has been observed. Multi-year studies are underway to further investigate the long-term effects of the disease.
COVID‑19 transmits when people breathe in air contaminated by droplets and small airborne particles containing the virus. The risk of breathing these in is highest when people are in close proximity, but they can be inhaled over longer distances, particularly indoors. Transmission can also occur if splashed or sprayed with contaminated fluids in the eyes, nose or mouth, and, rarely, via contaminated surfaces. People remain contagious for up to 20 days, and can spread the virus even if they do not develop symptoms.
Several testing methods have been developed to diagnose the disease. The standard diagnostic method is by detection of the virus’s nucleic acid by real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR), transcription-mediated amplification (TMA), or by reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) from a nasopharyngeal swab.
Several COVID-19 vaccines have been approved and distributed in various countries, which have initiated mass vaccination campaigns. Other preventive measures include physical or social distancing, quarantining, ventilation of indoor spaces, covering coughs and sneezes, hand washing, and keeping unwashed hands away from the face. The use of face masks or coverings has been recommended in public settings to minimize the risk of transmissions. While work is underway to develop drugs that inhibit the virus, the primary treatment is symptomatic. Management involves the treatment of symptoms, supportive care, isolation, and experimental measures.
Nomenclature
During the initial outbreak in Wuhan, the virus and disease were commonly referred to as “coronavirus” and “Wuhan coronavirus”, with the disease sometimes called “Wuhan pneumonia”. In the past, many diseases have been named after geographical locations, such as the Spanish flu, Middle East respiratory syndrome, and Zika virus. In January 2020, the WHO recommended 2019-nCoV and 2019-nCoV acute respiratory disease as interim names for the virus and disease per 2015 guidance and international guidelines against using geographical locations or groups of people in disease and virus names to prevent social stigma. The official names COVID‑19 and SARS-CoV-2 were issued by the WHO on 11 February 2020. Tedros Adhanom explained that CO stands for corona, VI for virus, D for disease, and 19 for 2019, the year in which the outbreak was first identified. The WHO additionally uses “the COVID‑19 virus” and “the virus responsible for COVID‑19” in public communications.
Signs and symptoms
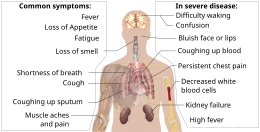
Symptoms of COVID-19
Symptoms of COVID-19 are variable, ranging from mild symptoms to severe illness. Common symptoms include headache, loss of smell (anosmia) and taste (ageusia), nasal congestion and runny nose, cough, muscle pain, sore throat, fever, diarrhea, and breathing difficulties. People with the same infection may have different symptoms, and their symptoms may change over time. Three common clusters of symptoms have been identified: one respiratory symptom cluster with cough, sputum, shortness of breath, and fever; a musculoskeletal symptom cluster with muscle and joint pain, headache, and fatigue; a cluster of digestive symptoms with abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea. In people without prior ear, nose, and throat disorders, loss of taste combined with loss of smell is associated with COVID-19 and is reported in as many as 88% of cases.
Of people who show symptoms, 81% develop only mild to moderate symptoms (up to mild pneumonia), while 14% develop severe symptoms (dyspnea, hypoxia, or more than 50% lung involvement on imaging) and 5% of patients suffer critical symptoms (respiratory failure, shock, or multiorgan dysfunction). At least a third of the people who are infected with the virus do not develop noticeable symptoms at any point in time. These asymptomatic carriers tend not to get tested and can spread the disease. Other infected people will develop symptoms later, called “pre-symptomatic”, or have very mild symptoms and can also spread the virus.
As is common with infections, there is a delay between the moment a person first becomes infected and the appearance of the first symptoms. The median delay for COVID-19 is four to five days. Most symptomatic people experience symptoms within two to seven days after exposure, and almost all will experience at least one symptom within 12 days.
Most people recover from the acute phase of the disease. However, some people – over half of a cohort of home-isolated young adults – continue to experience a range of effects, such as fatigue, for months after recovery, a condition called long COVID; long-term damage to organs has been observed. Multi-year studies are underway to further investigate the long-term effects of the disease.
Cause
COVID‑19 is caused by infection with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus strain.
Transmission

Transmission of COVID‑19
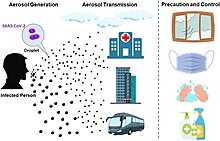
COVID-19 is mainly transmitted when people breathe in air contaminated by droplets and small airborne particles containing the virus. Infected people exhale those particles as they breathe, talk, cough, sneeze, or sing. Transmission is more likely when people are physically close. However, infection can occur over longer distances, particularly indoors.
Infectivity can occur 1-3 days before the onset of symptoms. Infected persons can spread the disease even if they are pre-symptomatic or asymptomatic. Most commonly, the peak viral load in upper respiratory tract samples occurs close to the time of symptom onset and declines after the first week after symptoms begin. Current evidence suggests a duration of viral shedding and the period of infectiousness of up to 10 days following symptom onset for persons with mild to moderate COVID-19, and a up to 20 days for persons with severe COVID-19, including immunocompromised persons.
Infectious particles range in size from aerosols that remain suspended in the air for long periods of time to larger droplets that remain airborne or fall to the ground. Additionally, COVID-19 research has redefined the traditional understanding of how respiratory viruses are transmitted. The largest droplets of respiratory fluid do not travel far, and can be inhaled or land on mucous membranes on the eyes, nose, or mouth to infect. Aerosols are highest in concentration when people are in close proximity, which leads to easier viral transmission when people are physically close, but airborne transmission can occur at longer distances, mainly in locations that are poorly ventilated; in those conditions small particles can remain suspended in the air for minutes to hours.
The number of people generally infected by one infected person varies; as only 10 to 20% of people are responsible for the disease’s spread. It often spreads in clusters, where infections can be traced back to an index case or geographical location. Often in these instances, superspreading events occur, where many people are infected by one person.
Virology

Illustration of SARSr-CoV virion
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. It was first isolated from three people with pneumonia connected to the cluster of acute respiratory illness cases in Wuhan. All structural features of the novel SARS-CoV-2 virus particle occur in related coronaviruses in nature.
Outside the human body, the virus is destroyed by household soap, which bursts its protective bubble.
SARS-CoV-2 is closely related to the original SARS-CoV. It is thought to have an animal (zoonotic) origin. Genetic analysis has revealed that the coronavirus genetically clusters with the genus Betacoronavirus, in subgenus Sarbecovirus (lineage B) together with two bat-derived strains. It is 96% identical at the whole genome level to other bat coronavirus samples (BatCov RaTG13). The structural proteins of SARS-CoV-2 include membrane glycoprotein (M), envelope protein (E), nucleocapsid protein (N), and the spike protein (S). The M protein of SARS-CoV-2 is about 98% similar to the M protein of bat SARS-CoV, maintains around 98% homology with pangolin SARS-CoV, and has 90% homology with the M protein of SARS-CoV; whereas, the similarity is only around 38% with the M protein of MERS-CoV.
SARS-CoV-2 variants
The many thousands of SARS-CoV-2 variants are grouped into either clades or lineages. The WHO, in collaboration with partners, expert networks, national authorities, institutions and researchers, have established nomenclature systems for naming and tracking SARS-CoV-2 genetic lineages by GISAID, Nextstrain and Pango. At the present time, the expert group convened by WHO has recommended the labeling of variants using letters of the Greek Alphabet, for example, Alpha, Beta, Delta, and Gamma, giving the justification that they “will be easier and more practical to discussed by non-scientific audiences.” Nextstrain divides the variants into five clades (19A, 19B, 20A, 20B, and 20C), while GISAID divides them into seven (L, O, V, S, G, GH, and GR). The Pango tool groups variants into lineages, with many circulating lineages being classed under the B.1 lineage.
Several notable variants of SARS-CoV-2 emerged throughout 2020. Cluster 5 emerged among minks and mink farmers in Denmark. After strict quarantines and a mink euthanasia campaign, the cluster was assessed to no longer be circulating among humans in Denmark as of 1 February 2021.
As of December 2021, there are five dominant variants of SARS-CoV-2 spreading among global populations: the Alpha variant (B.1.1.7, formerly called the UK variant), first found in London and Kent, the Beta variant (B.1.351, formerly called the South Africa variant), the Gamma variant (P.1, formerly called the Brazil variant), the Delta variant (B.1.617.2, formerly called the India variant), and the Omicron variant (B.1.1.529), which had spread to 57 countries as of 7 December.
Pathophysiology

COVID‑19 pathogenesis
The SARS-CoV-2 virus can infect a wide range of cells and systems of the body. COVID‑19 is most known for affecting the upper respiratory tract (sinuses, nose, and throat) and the lower respiratory tract (windpipe and lungs). The lungs are the organs most affected by COVID‑19 because the virus accesses host cells via the receptor for the enzyme angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), which is most abundant on the surface of type II alveolar cells of the lungs. The virus uses a special surface glycoprotein called a “spike” to connect to the ACE2 receptor and enter the host cell.
Respiratory tract
Following viral entry, COVID‑19 infects the ciliated epithelium of the nasopharynx and upper airways.
Nervous system
One common symptom, loss of smell, results from infection of the support cells of the olfactory epithelium, with subsequent damage to the olfactory neurons. The involvement of both the central and peripheral nervous system in COVID‑19 has been reported in many medical publications. It is clear that many people with COVID-19 exhibit neurological or mental health issues. The virus is not detected in the CNS of the majority of COVID-19 patients with neurological issues. However, SARS-CoV-2 has been detected at low levels in the brains of those who have died from COVID‑19, but these results need to be confirmed. While virus has been detected in cerebrospinal fluid of autopsies, the exact mechanism by which it invades the CNS remains unclear and may first involve invasion of peripheral nerves given the low levels of ACE2 in the brain. The virus may also enter the bloodstream from the lungs and cross the blood-brain barrier to gain access to the CNS, possibly within an infected white blood cell.

Tropism and multiple organ injuries in SARS-CoV-2 infection
Gastrointestinal tract
The virus also affects gastrointestinal organs as ACE2 is abundantly expressed in the glandular cells of gastric, duodenal and rectal epithelium as well as endothelial cells and enterocytes of the small intestine.
Cardiovascular system
The virus can cause acute myocardial injury and chronic damage to the cardiovascular system. An acute cardiac injury was found in 12% of infected people admitted to the hospital in Wuhan, China, and is more frequent in severe disease. Rates of cardiovascular symptoms are high, owing to the systemic inflammatory response and immune system disorders during disease progression, but acute myocardial injuries may also be related to ACE2 receptors in the heart. ACE2 receptors are highly expressed in the heart and are involved in heart function. A high incidence of thrombosis and venous thromboembolism have been found in people transferred to Intensive care units (ICU) with COVID‑19 infections, and may be related to poor prognosis. Blood vessel dysfunction and clot formation (as suggested by high D-dimer levels caused by blood clots) are thought to play a significant role in mortality, incidences of clots leading to pulmonary embolisms, and ischaemic events within the brain have been noted as complications leading to death in people infected with SARS-CoV-2. Infection appears to set off a chain of vasoconstrictive responses within the body, constriction of blood vessels within the pulmonary circulation has also been posited as a mechanism in which oxygenation decreases alongside the presentation of viral pneumonia. Furthermore, microvascular (arterioles and capillaries) blood vessel damage has been reported in a small number of tissue samples of the brains – without detected SARS-CoV-2 – and the olfactory bulbs from those who have died from COVID‑19. COVID‑19 was also found to cause substantial – including morphological and mechanical – changes to blood cells – such as increased sizes – sometimes persisting for months after hospital discharge.
Other organs
Another common cause of death is complications related to the kidneys. Early reports show that up to 30% of hospitalized patients both in China and in New York have experienced some injury to their kidneys, including some persons with no previous kidney problems.
Autopsies of people who died of COVID‑19 have found diffuse alveolar damage, and lymphocyte-containing inflammatory infiltrates within the lung.
Immunopathology

Key components of the adaptive immune response to SARS-CoV-2
Although SARS-CoV-2 has a tropism for ACE2-expressing epithelial cells of the respiratory tract, people with severe COVID‑19 have symptoms of systemic hyperinflammation. Clinical laboratory findings of elevated IL‑2, IL‑7, IL‑6, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM‑CSF), interferon gamma-induced protein 10 (IP‑10), monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP1), macrophage inflammatory protein 1‑alpha (MIP‑1‑alpha), and tumour necrosis factor (TNF‑α) indicative of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) suggest an underlying immunopathology.
Additionally, people with COVID‑19 and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) have classical serum biomarkers of CRS, including elevated C-reactive protein (CRP), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), D-dimer, and ferritin.
Systemic inflammation results in vasodilation, allowing inflammatory lymphocytic and monocytic infiltration of the lung and the heart. In particular, pathogenic GM-CSF-secreting T cells were shown to correlate with the recruitment of inflammatory IL-6-secreting monocytes and severe lung pathology in people with COVID‑19. Lymphocytic infiltrates have also been reported at autopsy.
Viral and host factors
Virus proteins

The association between SARS-CoV-2 and the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS)
Multiple viral and host factors affect the pathogenesis of the virus. The S-protein, otherwise known as the spike protein, is the viral component that attaches to the host receptor via the ACE2 receptors. It includes two subunits: S1 and S2. S1 determines the virus-host range and cellular tropism via the receptor-binding domain. S2 mediates the membrane fusion of the virus to its potential cell host via the H1 and HR2, which are heptad repeat regions. Studies have shown that S1 domain induced IgG and IgA antibody levels at a much higher capacity. It is the focus spike proteins expression that are involved in many effective COVID‑19 vaccines.
The M protein is the viral protein responsible for the transmembrane transport of nutrients. It is the cause of the bud release and the formation of the viral envelope. The N and E protein are accessory proteins that interfere with the host’s immune response.
Host factors
Human angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (hACE2) is the host factor that SARS-COV2 virus targets causing COVID‑19. Theoretically, the usage of angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB) and ACE inhibitors upregulating ACE2 expression might increase morbidity with COVID‑19, though animal data suggest some potential protective effect of ARB; however no clinical studies have proven susceptibility or outcomes. Until further data is available, guidelines and recommendations for hypertensive patients remain.
The effect of the virus on ACE2 cell surfaces leads to leukocytic infiltration, increased blood vessel permeability, alveolar wall permeability, as well as decreased secretion of lung surfactants. These effects cause the majority of the respiratory symptoms. However, the aggravation of local inflammation causes a cytokine storm eventually leading to a systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
Among healthy adults not exposed to SARS-CoV-2, about 35% have CD4+ T cells that recognize the SARS-CoV-2 S protein (particularly the S2 subunit) and about 50% react to other proteins of the virus, suggesting cross-reactivity from previous common colds caused by other coronaviruses.
It is unknown whether different persons use similar antibody genes in response to COVID‑19.
Host cytokine response
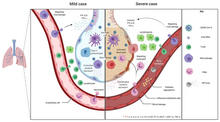
Mild versus severe immune response during virus infection
The severity of the inflammation can be attributed to the severity of what is known as the cytokine storm. Levels of interleukin 1B, interferon-gamma, interferon-inducible protein 10, and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 were all associated with COVID‑19 disease severity. Treatment has been proposed to combat the cytokine storm as it remains to be one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in COVID‑19 disease.
A cytokine storm is due to an acute hyperinflammatory response that is responsible for clinical illness in an array of diseases but in COVID‑19, it is related to worse prognosis and increased fatality. The storm causes acute respiratory distress syndrome, blood clotting events such as strokes, myocardial infarction, encephalitis, acute kidney injury, and vasculitis. The production of IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, TNF-alpha, and interferon-gamma, all crucial components of normal immune responses, inadvertently become the causes of a cytokine storm. The cells of the central nervous system, the microglia, neurons, and astrocytes, are also involved in the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines affecting the nervous system, and effects of cytokine storms toward the CNS are not uncommon.
Pregnancy response
There are many unknowns for pregnant women during the COVID‑19 pandemic. Given that they are prone to suffering from complications and severe disease infection with other types of coronaviruses, they have been identified as a vulnerable group and advised to take supplementary preventive measures.
Physiological responses to pregnancy can include:
- Immunological: The immunological response to COVID-19, like other viruses, depends on a working immune system. It adapts during pregnancy to allow the development of the fetus whose genetic load is only partially shared with their mother, leading to a different immunological reaction to infections during the course of pregnancy.
- Respiratory: Many factors can make pregnant women more vulnerable to hard respiratory infections. One of them is the total reduction of the lungs’ capacity and inability to clear secretions.
- Coagulation: During pregnancy, there are higher levels of circulating coagulation factors, and the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection can be implicated. The thromboembolic events with associated mortality are a risk for pregnant women.
However, from the evidence base, it is difficult to conclude whether pregnant women are at increased risk of grave consequences of this virus.
In addition to the above, other clinical studies have proved that SARS-CoV-2 can affect the period of pregnancy in different ways. On the one hand, there is little evidence of its impact up to 12 weeks gestation. On the other hand, COVID-19 infection may cause increased rates of unfavorable outcomes in the course of the pregnancy. Some examples of these could be fetal growth restriction, preterm birth, and perinatal mortality, which refers to the fetal death past 22 or 28 completed weeks of pregnancy as well as the death among live-born children up to seven completed days of life.
Unvaccinated women in later stages of pregnancy with COVID-19 are more likely than other patients to need very intensive care. Babies born to mothers with COVID-19 are more likely to have breathing problems. Pregnant women are strongly encouraged to get vaccinated.
Diagnosis
COVID‑19 can provisionally be diagnosed on the basis of symptoms and confirmed using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) or other nucleic acid testing of infected secretions. Along with laboratory testing, chest CT scans may be helpful to diagnose COVID‑19 in individuals with a high clinical suspicion of infection. Detection of a past infection is possible with serological tests, which detect antibodies produced by the body in response to the infection.
Viral testing

Demonstration of a nasopharyngeal swab for COVID‑19 testing
The standard methods of testing for presence of SARS-CoV-2 are nucleic acid tests, which detects the presence of viral RNA fragments. As these tests detect RNA but not infectious virus, its “ability to determine duration of infectivity of patients is limited.” The test is typically done on respiratory samples obtained by a nasopharyngeal swab; however, a nasal swab or sputum sample may also be used. Results are generally available within hours. The WHO has published several testing protocols for the disease.
Several laboratories and companies have developed serological tests, which detect antibodies produced by the body in response to infection. Several have been evaluated by Public Health England and approved for use in the UK.
The University of Oxford’s CEBM has pointed to mounting evidence that “a good proportion of ‘new’ mild cases and people re-testing positives after quarantine or discharge from hospital are not infectious, but are simply clearing harmless virus particles which their immune system has efficiently dealt with” and have called for “an international effort to standardize and periodically calibrate testing” On 7 September, the UK government issued “guidance for procedures to be implemented in laboratories to provide assurance of positive SARS-CoV-2 RNA results during periods of low prevalence, when there is a reduction in the predictive value of positive test results”.
Imaging
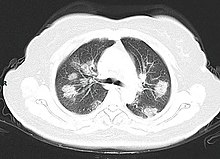
A CT scan of a person with COVID-19 shows lesions (bright regions) in the lungs

CT scan of rapid progression stage of COVID-19

Chest X-ray showing COVID‑19 pneumonia
Chest CT scans may be helpful to diagnose COVID‑19 in individuals with a high clinical suspicion of infection but are not recommended for routine screening. Bilateral multilobar ground-glass opacities with a peripheral, asymmetric, and posterior distribution are common in early infection. Subpleural dominance, crazy paving (lobular septal thickening with variable alveolar filling), and consolidation may appear as the disease progresses. Characteristic imaging features on chest radiographs and computed tomography (CT) of people who are symptomatic include asymmetric peripheral ground-glass opacities without pleural effusions.
Many groups have created COVID‑19 datasets that include imagery such as the Italian Radiological Society which has compiled an international online database of imaging findings for confirmed cases. Due to overlap with other infections such as adenovirus, imaging without confirmation by rRT-PCR is of limited specificity in identifying COVID‑19. A large study in China compared chest CT results to PCR and demonstrated that though imaging is less specific for the infection, it is faster and more sensitive.
Coding
In late 2019, the WHO assigned emergency ICD-10 disease codes U07.1 for deaths from lab-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and U07.2 for deaths from clinically or epidemiologically diagnosed COVID‑19 without lab-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Pathology
The main pathological findings at autopsy are:
- Macroscopy: pericarditis, lung consolidation and pulmonary oedema
- Lung findings:
- minor serous exudation, minor fibrin exudation
- pulmonary oedema, pneumocyte hyperplasia, large atypical pneumocytes, interstitial inflammation with lymphocytic infiltration and multinucleated giant cell formation
- diffuse alveolar damage (DAD) with diffuse alveolar exudates. DAD is the cause of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and severe hypoxemia.
- organisation of exudates in alveolar cavities and pulmonary interstitial fibrosis
- plasmocytosis in BAL
- Blood and vessels: disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC); leukoerythroblastic reaction, endotheliitis, hemophagocytosis
- Heart: cardiac muscle cell necrosis
- Liver: microvesicular steatosis
- Nose: shedding of olfactory epithelium
- Brain: infarction
- Kidneys: acute tubular damage.
- Spleen: white pulp depletion.
Prevention
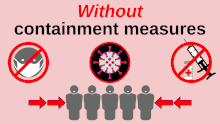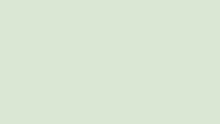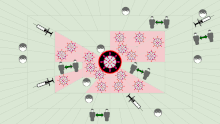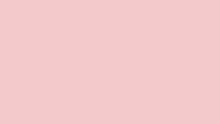
Without pandemic containment measures – such as social distancing, vaccination, and face masks – pathogens can spread exponentially. This graphic shows how early adoption of containment measures tends to protect wider swaths of the population.
Preventive measures to reduce the chances of infection include getting vaccinated, staying at home, wearing a mask in public, avoiding crowded places, keeping distance from others, ventilating indoor spaces, managing potential exposure durations, washing hands with soap and water often and for at least twenty seconds, practising good respiratory hygiene, and avoiding touching the eyes, nose, or mouth with unwashed hands.
Those diagnosed with COVID‑19 or who believe they may be infected are advised by the CDC to stay home except to get medical care, call ahead before visiting a healthcare provider, wear a face mask before entering the healthcare provider’s office and when in any room or vehicle with another person, cover coughs and sneezes with a tissue, regularly wash hands with soap and water and avoid sharing personal household items.
The first COVID‑19 vaccine was granted regulatory approval on 2 December 2020 by the UK medicines regulator MHRA. It was evaluated for emergency use authorization (EUA) status by the US FDA, and in several other countries. Initially, the US National Institutes of Health guidelines do not recommend any medication for prevention of COVID‑19, before or after exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus, outside the setting of a clinical trial. Without a vaccine, other prophylactic measures, or effective treatments, a key part of managing COVID‑19 is trying to decrease and delay the epidemic peak, known as “flattening the curve”. This is done by slowing the infection rate to decrease the risk of health services being overwhelmed, allowing for better treatment of active cases, and delaying additional cases until effective treatments or a vaccine become available.
Vaccine

COVID-19 Vaccination Center of the Medical University of Gdańsk, Poland

Different vaccine candidate types in development for SARS-CoV-2
A COVID‑19 vaccine is a vaccine intended to provide acquired immunity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‑19). Prior to the COVID‑19 pandemic, an established body of knowledge existed about the structure and function of coronaviruses causing diseases like severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). This knowledge accelerated the development of various vaccine platforms during early 2020. The initial focus of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines was on preventing symptomatic, often severe illness. On 10 January 2020, the SARS-CoV-2 genetic sequence data was shared through GISAID, and by 19 March, the global pharmaceutical industry announced a major commitment to address COVID‑19. The COVID‑19 vaccines are widely credited for their role in reducing the severity and death caused by COVID‑19.
Many countries have implemented phased distribution plans that prioritize those at highest risk of complications, such as the elderly, and those at high risk of exposure and transmission, such as healthcare workers.
As of 9 January 2022, 9.43 billion doses of COVID‑19 vaccines have been administered worldwide based on official reports from national public health agencies. By December 2020, more than 10 billion vaccine doses had been preordered by countries, with about half of the doses purchased by high-income countries comprising 14% of the world’s population.
Face masks and respiratory hygiene

Masks with an exhalation valve. The valves are a weak point that can transmit the viruses outwards.
The WHO and the US CDC recommend individuals wear non-medical face coverings in public settings where there is an increased risk of transmission and where social distancing measures are difficult to maintain. This recommendation is meant to reduce the spread of the disease by asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic individuals and is complementary to established preventive measures such as social distancing. Face coverings limit the volume and travel distance of expiratory droplets dispersed when talking, breathing, and coughing. A face covering without vents or holes will also filter out particles containing the virus from inhaled and exhaled air, reducing the chances of infection. But, if the mask include an exhalation valve, a wearer that is infected (maybe without having noticed that, and asymptomatic) would transmit the virus outwards through it, despite any certification they can have. So the masks with exhalation valve are not for the infected wearers, and are not reliable to stop the pandemic in a large scale. Many countries and local jurisdictions encourage or mandate the use of face masks or cloth face coverings by members of the public to limit the spread of the virus.
Masks are also strongly recommended for those who may have been infected and those taking care of someone who may have the disease. When not wearing a mask, the CDC recommends covering the mouth and nose with a tissue when coughing or sneezing and recommends using the inside of the elbow if no tissue is available. Proper hand hygiene after any cough or sneeze is encouraged. Healthcare professionals interacting directly with people who have COVID‑19 are advised to use respirators at least as protective as NIOSH-certified N95 or equivalent, in addition to other personal protective equipment.
Indoor ventilation and avoiding crowded indoor spaces
The CDC recommends that crowded indoor spaces should be avoided. When indoors, increasing the rate of air change, decreasing recirculation of air and increasing the use of outdoor air can reduce transmission. The WHO recommends ventilation and air filtration in public spaces to help clear out infectious aerosols.
Exhaled respiratory particles can build-up within enclosed spaces with inadequate ventilation. The risk of COVID‑19 infection increases especially in spaces where people engage in physical exertion or raise their voice (e.g., exercising, shouting, singing) as this increases exhalation of respiratory droplets. Prolonged exposure to these conditions, typically more than 15 minutes, leads to higher risk of infection.
Displacement ventilation with large natural inlets can move stale air directly to the exhaust in laminar flow while significantly reducing the concentration of droplets and particles. Passive ventilation reduces energy consumption and maintenance costs but may lack controllability and heat recovery. Displacement ventilation can also be achieved mechanically with higher energy and maintenance costs. The use of large ducts and openings helps to prevent mixing in closed environments. Recirculation and mixing should be avoided because recirculation prevents dilution of harmful particles and redistributes possibly contaminated air, and mixing increases the concentration and range of infectious particles and keeps larger particles in the air.
Hand-washing and hygiene

Students in Rwanda hand washing and wearing face masks during the COVID‑19 pandemic in the country.
Thorough hand hygiene after any cough or sneeze is required. The WHO also recommends that individuals wash hands often with soap and water for at least twenty seconds, especially after going to the toilet or when hands are visibly dirty, before eating and after blowing one’s nose. When soap and water are not available, the CDC recommends using an alcohol-based hand sanitiser with at least 60% alcohol. For areas where commercial hand sanitisers are not readily available, the WHO provides two formulations for local production. In these formulations, the antimicrobial activity arises from ethanol or isopropanol. Hydrogen peroxide is used to help eliminate bacterial spores in the alcohol; it is “not an active substance for hand antisepsis.” Glycerol is added as a humectant.
Social distancing
Social distancing (also known as physical distancing) includes infection control actions intended to slow the spread of the disease by minimising close contact between individuals. Methods include quarantines; travel restrictions; and the closing of schools, workplaces, stadiums, theatres, or shopping centres. Individuals may apply social distancing methods by staying at home, limiting travel, avoiding crowded areas, using no-contact greetings, and physically distancing themselves from others. Many governments are now mandating or recommending social distancing in regions affected by the outbreak.
Outbreaks have occurred in prisons due to crowding and an inability to enforce adequate social distancing. In the United States, the prisoner population is aging and many of them are at high risk for poor outcomes from COVID‑19 due to high rates of coexisting heart and lung disease, and poor access to high-quality healthcare.
Surface cleaning
After being expelled from the body, coronaviruses can survive on surfaces for hours to days. If a person touches the dirty surface, they may deposit the virus at the eyes, nose, or mouth where it can enter the body and cause infection. Evidence indicates that contact with infected surfaces is not the main driver of COVID‑19, leading to recommendations for optimised disinfection procedures to avoid issues such as the increase of antimicrobial resistance through the use of inappropriate cleaning products and processes. Deep cleaning and other surface sanitation has been criticized as hygiene theater, giving a false sense of security against something primarily spread through the air.
The amount of time that the virus can survive depends significantly on the type of surface, the temperature, and the humidity. Coronaviruses die very quickly when exposed to the UV light in sunlight. Like other enveloped viruses, SARS-CoV-2 survives longest when the temperature is at room temperature or lower, and when the relative humidity is low (<50%).
On many surfaces, including glass, some types of plastic, stainless steel, and skin, the virus can remain infective for several days indoors at room temperature, or even about a week under ideal conditions. On some surfaces, including cotton fabric and copper, the virus usually dies after a few hours. The virus dies faster on porous surfaces than on non-porous surfaces due to capillary action within pores and faster aerosol droplet evaporation. However, of the many surfaces tested, two with the longest survival times are N95 respirator masks and surgical masks, both of which are considered porous surfaces.
The CDC says that in most situations, cleaning surfaces with soap or detergent, not disinfecting, is enough to reduce risk of transmission. The CDC recommends that if a COVID‑19 case is suspected or confirmed at a facility such as an office or day care, all areas such as offices, bathrooms, common areas, shared electronic equipment like tablets, touch screens, keyboards, remote controls, and ATM machines used by the ill persons should be disinfected. Surfaces may be decontaminated with 62–71 percent ethanol, 50–100 percent isopropanol, 0.1 percent sodium hypochlorite, 0.5 percent hydrogen peroxide, and 0.2–7.5 percent povidone-iodine. Other solutions, such as benzalkonium chloride and chlorhexidine gluconate, are less effective. Ultraviolet germicidal irradiation may also be used. A datasheet comprising the authorised substances to disinfection in the food industry (including suspension or surface tested, kind of surface, use dilution, disinfectant and inocuylum volumes) can be seen in the supplementary material of.
Self-isolation
Self-isolation at home has been recommended for those diagnosed with COVID‑19 and those who suspect they have been infected. Health agencies have issued detailed instructions for proper self-isolation. Many governments have mandated or recommended self-quarantine for entire populations. The strongest self-quarantine instructions have been issued to those in high-risk groups. Those who may have been exposed to someone with COVID‑19 and those who have recently travelled to a country or region with the widespread transmission have been advised to self-quarantine for 14 days from the time of last possible exposure.
Healthy diet and lifestyle
The Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health recommends a healthy diet, being physically active, managing psychological stress, and getting enough sleep.
Consistently meeting scientific guidelines of 150+ minutes per week of exercise or similar physical activity was shown to be associated with a smaller risk of hospitalisation and death due to COVID‑19, even when considering likely risk factors such as elevated Body mass index (BMI).
A meta-analysis, published online in October 2021, concluded that “Vitamin D supplementation in SARS-CoV-2 positive patients has the potential to positively impact patients with both mild and severe symptoms.” The largest observational study on the subject using online questionnaires, with over 6 000 participants and a dosage regime near the RDI, is set to conclude in July 2021. One of the collaborators in the study is Synergy Biologics Ltd, a manufacturer of vitamin D3 supplements.
A 2021 Cochrane rapid review found that based upon low-certainty evidence, international travel-related control measures such as restricting cross-border travel may help to contain the spread of COVID‑19. Additionally, symptom/exposure-based screening measures at borders may miss many positive cases. While test-based border screening measures may be more effective, it could also miss many positive cases if only conducted upon arrival without follow-up. The review concluded that a minimum 10-day quarantine may be beneficial in preventing the spread of COVID‑19 and may be more effective if combined with an additional control measure like border screening.
Treatment

An overview of COVID-19 therapeutics and drugs
There is no specific, effective treatment or cure for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‑19), the disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. One year into the pandemic, highly effective vaccines have now been introduced and are beginning to slow the spread of SARS-CoV-2; however, for those awaiting vaccination, as well as for the estimated millions of immunocompromised persons who are unlikely to respond robustly to vaccination, treatment remains important. Thus, the lack of progress developing effective treatments means that the cornerstone of management of COVID‑19 has been supportive care, which includes treatment to relieve symptoms, fluid therapy, oxygen support and prone positioning as needed, and medications or devices to support other affected vital organs.
Most cases of COVID‑19 are mild. In these, supportive care includes medication such as paracetamol or NSAIDs to relieve symptoms (fever, body aches, cough), proper intake of fluids, rest, and nasal breathing. Good personal hygiene and a healthy diet are also recommended. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend that those who suspect they are carrying the virus isolate themselves at home and wear a face mask.
People with more severe cases may need treatment in hospital. In those with low oxygen levels, use of the glucocorticoid dexamethasone is strongly recommended, as it can reduce the risk of death. Noninvasive ventilation and, ultimately, admission to an intensive care unit for mechanical ventilation may be required to support breathing. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) has been used to address the issue of respiratory failure, but its benefits are still under consideration. Some of the cases of severe disease course are caused by systemic hyper-inflammation, the so-called cytokine storm.
Several experimental treatments are being actively studied in clinical trials. These include fluvoxamine, a cheap and widely available antidepressant; and the antivirals molnupiravir (developed by Merck), and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (developed by Pfizer). Others were thought to be promising early in the pandemic, such as hydroxychloroquine and lopinavir/ritonavir, but later research found them to be ineffective or even harmful. Despite ongoing research, there is still not enough high-quality evidence to recommend so-called early treatment. Nevertheless, in the United States, two monoclonal antibody-based therapies are available for early use in cases thought to be at high risk of progression to severe disease. The antiviral remdesivir is available in the U.S., Canada, Australia, and several other countries, with varying restrictions; however, it is not recommended for people needing mechanical ventilation, and is discouraged altogether by the World Health Organization (WHO), due to limited evidence of its efficacy. In November 2021, the UK approved the use of molnupiravir as a COVID treatment for vulnerable patients recently diagnosed with the disease.
Prognosis
The severity of COVID‑19 varies. The disease may take a mild course with few or no symptoms, resembling other common upper respiratory diseases such as the common cold. In 3–4% of cases (7.4% for those over age 65) symptoms are severe enough to cause hospitalization. Mild cases typically recover within two weeks, while those with severe or critical diseases may take three to six weeks to recover. Among those who have died, the time from symptom onset to death has ranged from two to eight weeks. The Italian Istituto Superiore di Sanità reported that the median time between the onset of symptoms and death was twelve days, with seven being hospitalised. However, people transferred to an ICU had a median time of ten days between hospitalisation and death. Prolonged prothrombin time and elevated C-reactive protein levels on admission to the hospital are associated with severe course of COVID‑19 and with a transfer to ICU.
Some early studies suggest 10% to 20% of people with COVID‑19 will experience symptoms lasting longer than a month. A majority of those who were admitted to hospital with severe disease report long-term problems including fatigue and shortness of breath. On 30 October 2020, WHO chief Tedros Adhanom warned that “to a significant number of people, the COVID virus poses a range of serious long-term effects.” He has described the vast spectrum of COVID‑19 symptoms that fluctuate over time as “really concerning”. They range from fatigue, a cough and shortness of breath, to inflammation and injury of major organs – including the lungs and heart, and also neurological and psychologic effects. Symptoms often overlap and can affect any system in the body. Infected people have reported cyclical bouts of fatigue, headaches, months of complete exhaustion, mood swings, and other symptoms. Tedros therefore concluded that a strategy of achieving herd immunity by infection, rather than vaccination, is “morally unconscionable and unfeasible”.
In terms of hospital readmissions about 9% of 106,000 individuals had to return for hospital treatment within two months of discharge. The average to readmit was eight days since first hospital visit. There are several risk factors that have been identified as being a cause of multiple admissions to a hospital facility. Among these are advanced age (above 65 years of age) and presence of a chronic condition such as diabetes, COPD, heart failure or chronic kidney disease.
According to scientific reviews smokers are more likely to require intensive care or die compared to non-smokers. Acting on the same ACE2 pulmonary receptors affected by smoking, air pollution has been correlated with the disease. Short term and chronic exposure to air pollution seems to enhance morbidity and mortality from COVID‑19. Pre-existing heart and lung diseases and also obesity, especially in conjunction with fatty liver disease, contributes to an increased health risk of COVID‑19.
It is also assumed that those that are immunocompromised are at higher risk of getting severely sick from SARS-CoV-2. One research that looked into the COVID‑19 infections in hospitalized kidney transplant recipients found a mortality rate of 11%.
Genetics also plays an important role in the ability to fight off the disease. For instance, those that do not produce detectable type I interferons or produce auto-antibodies against these may get much sicker from COVID‑19. Genetic screening is able to detect interferon effector genes.
Pregnant women may be at higher risk of severe COVID‑19 infection based on data from other similar viruses, like SARS and MERS, but data for COVID‑19 is lacking.
Children
While very young children have experienced lower rates of infection, older children have a rate of infection that is similar to the population as a whole. Children are likely to have milder symptoms and are at lower risk of severe disease than adults. The CDC reports that in the US roughly a third of hospitalized children were admitted to the ICU, while a European multinational study of hospitalized children from June 2020 found that about 8% of children admitted to a hospital needed intensive care. Four of the 582 children (0.7%) in the European study died, but the actual mortality rate may be “substantially lower” since milder cases that did not seek medical help were not included in the study.
Complications
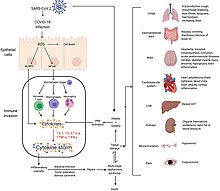
Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 cytokine storm and complications
Complications may include pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), multi-organ failure, septic shock, and death. Cardiovascular complications may include heart failure, arrhythmias (including atrial fibrillation), heart inflammation, and thrombosis, particularly venous thromboembolism. Approximately 20–30% of people who present with COVID‑19 have elevated liver enzymes, reflecting liver injury.
Neurologic manifestations include seizure, stroke, encephalitis, and Guillain–Barré syndrome (which includes loss of motor functions). Following the infection, children may develop paediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome, which has symptoms similar to Kawasaki disease, which can be fatal. In very rare cases, acute encephalopathy can occur, and it can be considered in those who have been diagnosed with COVID‑19 and have an altered mental status.
In the case of pregnant women, it is important to note that, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, pregnant women are at increased risk of becoming seriously ill from COVID‑19. This is because pregnant women with COVID‑19 appear to be more likely to develop respiratory and obstetric complications that can lead to miscarriage, premature delivery and intrauterine growth restriction.
Fungal infections such as aspergillosis, candidiasis, cryptococcosis and mucormycosis have been recorded in patients recovering from COVID‑19.
Longer-term effects
Some early studies suggest that 10–20% of people with COVID‑19 will experience symptoms lasting longer than a month. A majority of those who were admitted to hospital with severe disease report long-term problems, including fatigue and shortness of breath. About 5–10% of patients admitted to hospital progress to severe or critical disease, including pneumonia and acute respiratory failure.
By a variety of mechanisms, the lungs are the organs most affected in COVID‑19. In people requiring hospital admission, up to 98% of CT scans performed show lung abnormalities after 28 days of illness even if they had clinically improved.
People with advanced age, severe disease, prolonged ICU stays, or who smoke are more likely to have long-lasting effects, including pulmonary fibrosis. Overall, approximately one-third of those investigated after four weeks will have findings of pulmonary fibrosis or reduced lung function as measured by DLCO, even in asymptomatic people, but with the suggestion of continuing improvement with the passing of more time.
Immunity

Human antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 infection
The immune response by humans to SARS-CoV-2 virus occurs as a combination of the cell-mediated immunity and antibody production, just as with most other infections. B cells interact with T cells and begin dividing before selection into the plasma cell, partly on the basis of their affinity for antigen. Since SARS-CoV-2 has been in the human population only since December 2019, it remains unknown if the immunity is long-lasting in people who recover from the disease. The presence of neutralizing antibodies in blood strongly correlates with protection from infection, but the level of neutralizing antibody declines with time. Those with asymptomatic or mild disease had undetectable levels of neutralizing antibody two months after infection. In another study, the level of neutralizing antibodies fell four-fold one to four months after the onset of symptoms. However, the lack of antibodies in the blood does not mean antibodies will not be rapidly produced upon reexposure to SARS-CoV-2. Memory B cells specific for the spike and nucleocapsid proteins of SARS-CoV-2 last for at least six months after the appearance of symptoms.
Reinfection with COVID‑19 is possible but uncommon. The first case of reinfection was documented in August 2020. A systematic review found 17 cases of confirmed reinfection in medical literature as of May 2021.
Mortality
Several measures are commonly used to quantify mortality. These numbers vary by region and over time and are influenced by the volume of testing, healthcare system quality, treatment options, time since the initial outbreak, and population characteristics such as age, sex, and overall health.
The mortality rate reflects the number of deaths within a specific demographic group divided by the population of that demographic group. Consequently, the mortality rate reflects the prevalence as well as the severity of the disease within a given population. Mortality rates are highly correlated to age, with relatively low rates for young people and relatively high rates among the elderly. In fact, one relevant factor of mortality rates is the age structure of the countries’ populations. For example, the case fatality rate for COVID‑19 is lower in India than in the US since India’s younger population represents a larger percentage than in the US.
Case fatality rate
The case fatality rate (CFR) reflects the number of deaths divided by the number of diagnosed cases within a given time interval. Based on Johns Hopkins University statistics, the global death-to-case ratio is 1.79% (5,490,117/307,346,252) as of 10 January 2022. The number varies by region. The CFR may not reflect the true severity of the disease, because some infected individuals remain asymptomatic or experience only mild symptoms, and hence such infections may not be included in official case reports. Moreover, the CFR may vary markedly over time and across locations due to the availability of live virus tests.
-
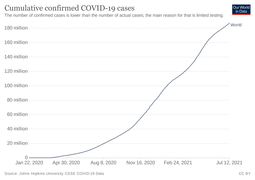
Total confirmed cases over time
-

Total confirmed cases of COVID‑19 per million people
-

Total deaths over time
-
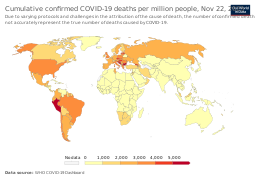
Total confirmed deaths due to COVID‑19 per million people
Infection fatality rate
A key metric in gauging the severity of COVID‑19 is the infection fatality rate (IFR), also referred to as the infection fatality ratio or infection fatality risk. This metric is calculated by dividing the total number of deaths from the disease by the total number of infected individuals; hence, in contrast to the CFR, the IFR incorporates asymptomatic and undiagnosed infections as well as reported cases.
Estimates
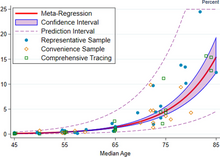
The red line shows the estimate of infection fatality rate (IFR), in percentage terms, as a function of age. The shaded region depicts the 95% confidence interval for that estimate. Markers denotes specific observations used in the meta-analysis.

The same relationship plotted on a log scale
A December 2020 systematic review and meta-analysis estimated that population IFR during the first wave of the pandemic was about 0.5% to 1% in many locations (including France, Netherlands, New Zealand, and Portugal), 1% to 2% in other locations (Australia, England, Lithuania, and Spain), and exceeded 2% in Italy. That study also found that most of these differences in IFR reflected corresponding differences in the age composition of the population and age-specific infection rates; in particular, the metaregression estimate of IFR is very low for children and younger adults (e.g., 0.002% at age 10 and 0.01% at age 25) but increases progressively to 0.4% at age 55, 1.4% at age 65, 4.6% at age 75, and 15% at age 85. These results were also highlighted in a December 2020 report issued by the WHO.
| Age group | IFR |
|---|---|
| 0–34 | 0.004% |
| 35–44 | 0.068% |
| 45–54 | 0.23% |
| 55–64 | 0.75% |
| 65–74 | 2.5% |
| 75–84 | 8.5% |
| 85 + | 28.3% |
An analysis of those IFR rates indicates that COVID‑19 is hazardous not only for the elderly but also for middle-aged adults, for whom a fatal COVID‑19 infection is two orders of magnitude more likely than the annualized risk of a fatal automobile accident and far more dangerous than seasonal influenza.
Earlier estimates of IFR
At an early stage of the pandemic, the World Health Organization reported estimates of IFR between 0.3% and 1%. On 2 July, The WHO’s chief scientist reported that the average IFR estimate presented at a two-day WHO expert forum was about 0.6%. In August, the WHO found that studies incorporating data from broad serology testing in Europe showed IFR estimates converging at approximately 0.5–1%. Firm lower limits of IFRs have been established in a number of locations such as New York City and Bergamo in Italy since the IFR cannot be less than the population fatality rate. (After sufficient time however, people can get reinfected). As of 10 July, in New York City, with a population of 8.4 million, 23,377 individuals (18,758 confirmed and 4,619 probable) have died with COVID‑19 (0.3% of the population). Antibody testing in New York City suggested an IFR of ~0.9%, and ~1.4%. In Bergamo province, 0.6% of the population has died. In September 2020, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported preliminary estimates of age-specific IFRs for public health planning purposes.
Sex differences
COVID‑19 case fatality rates are higher among men than women in most countries. However, in a few countries like India, Nepal, Vietnam, and Slovenia the fatality cases are higher in women than men. Globally, men are more likely to be admitted to the ICU and more likely to die. One meta-analysis found that globally, men were more likely to get COVID‑19 than women; there were approximately 55 men and 45 women per 100 infections (CI: 51.43–56.58).
The Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention reported the death rate was 2.8% for men and 1.7% for women. Later reviews in June 2020 indicated that there is no significant difference in susceptibility or in CFR between genders. One review acknowledges the different mortality rates in Chinese men, suggesting that it may be attributable to lifestyle choices such as smoking and drinking alcohol rather than genetic factors. Smoking, which in some countries like China is mainly a male activity, is a habit that contributes to increasing significantly the case fatality rates among men. Sex-based immunological differences, lesser prevalence of smoking in women and men developing co-morbid conditions such as hypertension at a younger age than women could have contributed to the higher mortality in men. In Europe as of February 2020, 57% of the infected people were men and 72% of those died with COVID‑19 were men. As of April 2020, the US government is not tracking sex-related data of COVID‑19 infections. Research has shown that viral illnesses like Ebola, HIV, influenza and SARS affect men and women differently.
Ethnic differences
In the US, a greater proportion of deaths due to COVID‑19 have occurred among African Americans and other minority groups. Structural factors that prevent them from practicing social distancing include their concentration in crowded substandard housing and in “essential” occupations such as retail grocery workers, public transit employees, health-care workers and custodial staff. Greater prevalence of lacking health insurance and care of underlying conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease also increase their risk of death. Similar issues affect Native American and Latino communities. On the one hand, in the Dominican Republic there is a clear example of both gender and ethnic inequality. In this Latin American territory, there is great inequality and precariousness that especially affects Dominican women, with greater emphasis on those of Haitian descent. According to a US health policy non-profit, 34% of American Indian and Alaska Native People (AIAN) non-elderly adults are at risk of serious illness compared to 21% of white non-elderly adults. The source attributes it to disproportionately high rates of many health conditions that may put them at higher risk as well as living conditions like lack of access to clean water.
Leaders have called for efforts to research and address the disparities. In the UK, a greater proportion of deaths due to COVID‑19 have occurred in those of a Black, Asian, and other ethnic minority background. More severe impacts upon victims including the relative incidence of the necessity of hospitalization requirements, and vulnerability to the disease has been associated via DNA analysis to be expressed in genetic variants at chromosomal region 3, features that are associated with European Neanderthal heritage. That structure imposes greater risks that those affected will develop a more severe form of the disease. The findings are from Professor Svante Pääbo and researchers he leads at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology and the Karolinska Institutet. This admixture of modern human and Neanderthal genes is estimated to have occurred roughly between 50,000 and 60,000 years ago in Southern Europe.
Comorbidities
Biological factors (immune response) and the general behaviour (habits) can strongly determine the consequences of COVID‑19. Most of those who die of COVID‑19 have pre-existing (underlying) conditions, including hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease. According to March data from the United States, 89% of those hospitalised had preexisting conditions. The Italian Istituto Superiore di Sanità reported that out of 8.8% of deaths where medical charts were available, 96.1% of people had at least one comorbidity with the average person having 3.4 diseases. According to this report the most common comorbidities are hypertension (66% of deaths), type 2 diabetes (29.8% of deaths), Ischemic Heart Disease (27.6% of deaths), atrial fibrillation (23.1% of deaths) and chronic renal failure (20.2% of deaths).
Most critical respiratory comorbidities according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), are: moderate or severe asthma, pre-existing COPD, pulmonary fibrosis, cystic fibrosis. Evidence stemming from meta-analysis of several smaller research papers also suggests that smoking can be associated with worse outcomes. When someone with existing respiratory problems is infected with COVID‑19, they might be at greater risk for severe symptoms. COVID‑19 also poses a greater risk to people who misuse opioids and methamphetamines, insofar as their drug use may have caused lung damage.
In August 2020, the CDC issued a caution that tuberculosis (TB) infections could increase the risk of severe illness or death. The WHO recommended that people with respiratory symptoms be screened for both diseases, as testing positive for COVID‑19 could not rule out co-infections. Some projections have estimated that reduced TB detection due to the pandemic could result in 6.3 million additional TB cases and 1.4 million TB-related deaths by 2025.
History
The virus is thought to be of natural animal origin, most likely through spillover infection. There are several theories about where the index case originated and investigations into the origin of the pandemic are ongoing. Phylogenetics estimates that SARS-CoV-2 arose in October or November 2019. A phylogenetic algorithm analysis suggested that the virus may have been circulating in Guangdong before Wuhan. Evidence suggests that it descends from a coronavirus that infects wild bats, and spread to humans through an intermediary wildlife host. The possibility that the virus was accidentally released from a laboratory is also under increasingly active consideration. U.S intelligence agencies found that the virus was not developed as a biological weapon and that it’s unlikely for it to have been genetically engineered.
The first confirmed human infections were in Wuhan, Hubei, China. A study of the first 41 cases of confirmed COVID‑19, published in January 2020 in The Lancet, reported the earliest date of onset of symptoms as 1 December 2019. Official publications from the WHO reported the earliest onset of symptoms as 8 December 2019. Human-to-human transmission was confirmed by the WHO and Chinese authorities by 20 January 2020. According to official Chinese sources, these were mostly linked to the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market, which also sold live animals. In May 2020, George Gao, the director of the CDC, said animal samples collected from the seafood market had tested negative for the virus, indicating that the market was the site of an early superspreading event, but that it was not the site of the initial outbreak. Traces of the virus have been found in wastewater samples that were collected in Milan and Turin, Italy, on 18 December 2019.
By December 2019, the spread of infection was almost entirely driven by human-to-human transmission. The number of coronavirus cases in Hubei gradually increased, reaching sixty by 20 December, and at least 266 by 31 December. On 24 December, Wuhan Central Hospital sent a bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BAL) sample from an unresolved clinical case to sequencing company Vision Medicals. On 27 and 28 December, Vision Medicals informed the Wuhan Central Hospital and the Chinese CDC of the results of the test, showing a new coronavirus. A pneumonia cluster of unknown cause was observed on 26 December and treated by the doctor Zhang Jixian in Hubei Provincial Hospital, who informed the Wuhan Jianghan CDC on 27 December. On 30 December, a test report addressed to Wuhan Central Hospital, from company CapitalBio Medlab, stated an erroneous positive result for SARS, causing a group of doctors at Wuhan Central Hospital to alert their colleagues and relevant hospital authorities of the result. The Wuhan Municipal Health Commission issued a notice to various medical institutions on “the treatment of pneumonia of unknown cause” that same evening. Eight of these doctors, including Li Wenliang (punished on 3 January), were later admonished by the police for spreading false rumours and another, Ai Fen, was reprimanded by her superiors for raising the alarm.
The Wuhan Municipal Health Commission made the first public announcement of a pneumonia outbreak of unknown cause on 31 December, confirming 27 cases – enough to trigger an investigation.
During the early stages of the outbreak, the number of cases doubled approximately every seven and a half days. In early and mid-January 2020, the virus spread to other Chinese provinces, helped by the Chinese New Year migration and Wuhan being a transport hub and major rail interchange. On 20 January, China reported nearly 140 new cases in one day, including two people in Beijing and one in Shenzhen. Later official data shows 6,174 people had already developed symptoms by then, and more may have been infected. A report in The Lancet on 24 January indicated human transmission, strongly recommended personal protective equipment for health workers, and said testing for the virus was essential due to its “pandemic potential”. On 30 January, the WHO declared the coronavirus a Public Health Emergency of International Concern. By this time, the outbreak spread by a factor of 100 to 200 times.
Italy had its first confirmed cases on 31 January 2020, two tourists from China. Italy overtook China as the country with the most deaths on 19 March 2020 . By 26 March the United States had overtaken China and Italy with the highest number of confirmed cases in the world. Research on coronavirus genomes indicates the majority of COVID-19 cases in New York came from European travellers, rather than directly from China or any other Asian country. Retesting of prior samples found a person in France who had the virus on 27 December 2019, and a person in the United States who died from the disease on 6 February 2020.
RT-PCR testing of untreated wastewater samples from Brazil and Italy have suggested detection of SARS-CoV-2 as early as November and December 2019, respectively, but the methods of such sewage studies have not been optimised, many have not been peer-reviewed, details are often missing, and there is a risk of false positives due to contamination or if only one gene target is detected. A September 2020 review journal article said, “The possibility that the COVID‑19 infection had already spread to Europe at the end of last year is now indicated by abundant, even if partially circumstantial, evidence,” including pneumonia case numbers and radiology in France and Italy in November and December.
As of 1 October 2021, Reuters reported that it had estimated the worldwide total number of deaths due to COVID‑19 to have exceeded five million.
Misinformation
After the initial outbreak of COVID‑19, misinformation and disinformation regarding the origin, scale, prevention, treatment, and other aspects of the disease rapidly spread online.
In September 2020, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published preliminary estimates of the risk of death by age groups in the United States, but those estimates were widely misreported and misunderstood.
Other species
Humans appear to be capable of spreading the virus to some other animals, a type of disease transmission referred to as zooanthroponosis.
Some pets, especially cats and ferrets, can catch this virus from infected humans. Symptoms in cats include respiratory (such as a cough) and digestive symptoms. Cats can spread the virus to other cats, and may be able to spread the virus to humans, but cat-to-human transmission of SARS-CoV-2 has not been proven. Compared to cats, dogs are less susceptible to this infection. Behaviors which increase the risk of transmission include kissing, licking, and petting the animal.
The virus does not appear to be able to infect pigs, ducks, or chickens at all. Mice, rats, and rabbits, if they can be infected at all, are unlikely to be involved in spreading the virus.
Tigers and lions in zoos have become infected as a result of contact with infected humans. As expected, monkeys and great ape species such as orangutans can also be infected with the COVID‑19 virus.
Minks, which are in the same family as ferrets, have been infected. Minks may be asymptomatic, and can also spread the virus to humans. Multiple countries have identified infected animals in mink farms. Denmark, a major producer of mink pelts, ordered the slaughter of all minks over fears of viral mutations, following an outbreak referred to as Cluster 5. A vaccine for mink and other animals is being researched.
Research
International research on vaccines and medicines in COVID‑19 is underway by government organisations, academic groups, and industry researchers. The CDC has classified it to require a BSL3 grade laboratory. There has been a great deal of COVID‑19 research, involving accelerated research processes and publishing shortcuts to meet the global demand.
As of December 2020, hundreds of clinical trials have been undertaken, with research happening on every continent except Antarctica. As of November 2020, more than 200 possible treatments had been studied in humans so far.
Transmission and prevention research
Modelling research has been conducted with several objectives, including predictions of the dynamics of transmission, diagnosis and prognosis of infection, estimation of the impact of interventions, or allocation of resources. Modelling studies are mostly based on compartmental models in epidemiology, estimating the number of infected people over time under given conditions. Several other types of models have been developed and used during the COVID‑19 including computational fluid dynamics models to study the flow physics of COVID‑19, retrofits of crowd movement models to study occupant exposure, mobility-data based models to investigate transmission, or the use of macroeconomic models to assess the economic impact of the pandemic. Further, conceptual frameworks from crisis management research have been applied to better understand the effects of COVID‑19 on organizations worldwide.
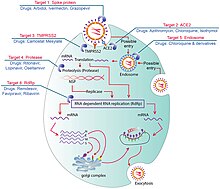
Seven possible drug targets in viral replication process and drugs
Repurposed antiviral drugs make up most of the research into COVID‑19 treatments. Other candidates in trials include vasodilators, corticosteroids, immune therapies, lipoic acid, bevacizumab, and recombinant angiotensin-converting enzyme 2.
In March 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) initiated the Solidarity trial to assess the treatment effects of some promising drugs: an experimental drug called remdesivir; anti-malarial drugs chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine; two anti-HIV drugs, lopinavir/ritonavir; and interferon-beta. More than 300 active clinical trials are underway as of April 2020.
Research on the antimalarial drugs hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine showed that they were ineffective at best, and that they may reduce the antiviral activity of remdesivir. By May 2020, France, Italy, and Belgium had banned the use of hydroxychloroquine as a COVID‑19 treatment.
In June, initial results from the randomised RECOVERY Trial in the United Kingdom showed that dexamethasone reduced mortality by one third for people who are critically ill on ventilators and one fifth for those receiving supplemental oxygen. Because this is a well-tested and widely available treatment, it was welcomed by the WHO, which is in the process of updating treatment guidelines to include dexamethasone and other steroids. Based on those preliminary results, dexamethasone treatment has been recommended by the NIH for patients with COVID‑19 who are mechanically ventilated or who require supplemental oxygen but not in patients with COVID‑19 who do not require supplemental oxygen.
In September 2020, the WHO released updated guidance on using corticosteroids for COVID‑19. The WHO recommends systemic corticosteroids rather than no systemic corticosteroids for the treatment of people with severe and critical COVID‑19 (strong recommendation, based on moderate certainty evidence). The WHO suggests not to use corticosteroids in the treatment of people with non-severe COVID‑19 (conditional recommendation, based on low certainty evidence). The updated guidance was based on a meta-analysis of clinical trials of critically ill COVID‑19 patients.
In September 2020, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) endorsed the use of dexamethasone in adults and adolescents from twelve years of age and weighing at least 40 kilograms (88 lb) who require supplemental oxygen therapy. Dexamethasone can be taken by mouth or given as an injection or infusion (drip) into a vein.
In November 2020, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued an emergency use authorization for the investigational monoclonal antibody therapy bamlanivimab for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID‑19. Bamlanivimab is authorized for people with positive results of direct SARS-CoV-2 viral testing who are twelve years of age and older weighing at least 40 kilograms (88 lb), and who are at high risk for progressing to severe COVID‑19 or hospitalization. This includes those who are 65 years of age or older, or who have chronic medical conditions.
In February 2021, the FDA issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for bamlanivimab and etesevimab administered together for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID‑19 in people twelve years of age or older weighing at least 40 kilograms (88 lb) who test positive for SARS‑CoV‑2 and who are at high risk for progressing to severe COVID‑19. The authorized use includes treatment for those who are 65 years of age or older or who have certain chronic medical conditions.
In April 2021, the FDA revoked the emergency use authorization (EUA) that allowed for the investigational monoclonal antibody therapy bamlanivimab, when administered alone, to be used for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID‑19 in adults and certain pediatric patients.
Cytokine storm

Various therapeutic strategies for targeting cytokine storm
A cytokine storm can be a complication in the later stages of severe COVID‑19. A cytokine storm is a potentially deadly immune reaction where a large amount of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines are released too quickly. A cytokine storm can lead to ARDS and multiple organ failure. Data collected from Jin Yin-tan Hospital in Wuhan, China indicates that patients who had more severe responses to COVID‑19 had greater amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in their system than patients who had milder responses. These high levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines indicate presence of a cytokine storm.
Tocilizumab has been included in treatment guidelines by China’s National Health Commission after a small study was completed. It is undergoing a Phase II non-randomised trial at the national level in Italy after showing positive results in people with severe disease. Combined with a serum ferritin blood test to identify a cytokine storm (also called cytokine storm syndrome, not to be confused with cytokine release syndrome), it is meant to counter such developments, which are thought to be the cause of death in some affected people. The interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R) antagonist was approved by the FDA to undergo a Phase III clinical trial assessing its effectiveness on COVID‑19 based on retrospective case studies for the treatment of steroid-refractory cytokine release syndrome induced by a different cause, CAR T cell therapy, in 2017. There is no randomised, controlled evidence that tocilizumab is an efficacious treatment for CRS. Prophylactic tocilizumab has been shown to increase serum IL-6 levels by saturating the IL-6R, driving IL-6 across the blood-brain barrier, and exacerbating neurotoxicity while having no effect on the incidence of CRS.
Lenzilumab, an anti-GM-CSF monoclonal antibody, is protective in murine models for CAR T cell-induced CRS and neurotoxicity and is a viable therapeutic option due to the observed increase of pathogenic GM-CSF secreting T cells in hospitalised patients with COVID‑19.
Passive antibodies

Overview of the application and use of convalescent plasma therapy
Transferring purified and concentrated antibodies produced by the immune systems of those who have recovered from COVID‑19 to people who need them is being investigated as a non-vaccine method of passive immunisation. Viral neutralization is the anticipated mechanism of action by which passive antibody therapy can mediate defence against SARS-CoV-2. The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 is the primary target for neutralizing antibodies. As of 8 August 2020, eight neutralizing antibodies targeting the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 have entered clinical studies. It has been proposed that selection of broad-neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV might be useful for treating not only COVID‑19 but also future SARS-related CoV infections. Other mechanisms, however, such as antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity or phagocytosis, may be possible. Other forms of passive antibody therapy, for example, using manufactured monoclonal antibodies, are in development.
The use of passive antibodies to treat people with active COVID‑19 is also being studied. This involves the production of convalescent serum, which consists of the liquid portion of the blood from people who recovered from the infection and contains antibodies specific to this virus, which is then administered to active patients. This strategy was tried for SARS with inconclusive results. An updated Cochrane review in May 2021, found high certainty evidence that for the treatment of people with moderate to severe COVID‑19 convalescent plasma did not reduce mortality or bring about symptom improvement There continues to be uncertainty about the safety of convalescent plasma administration to people with COVID‑19 and differing outcomes measured in different studies limits their use in determining efficacy.
Bioethics
Since the outbreak of the COVID‑19 pandemic, scholars have explored the bioethics, normative economics, and political theories of healthcare policies related to the public health crisis. Academics have pointed to the moral distress of healthcare workers, ethics of distributing scarce healthcare resources such as ventilators, and the global justice of vaccine diplomacies. The socio-economic inequalities between genders, races, groups with disabilities, communities, regions, countries, and continents have also drawn attention in academia and the general public.
Effect on other diseases and the pharmacy trade
There was a report on 3 March 2021, that social distancing and common wearing of surgical masks and similar as a common precaution against COVID‑19 caused a drop in the spread rate of the common cold and flu. So much so, that in Britain the sale of cough liquids and throat lozenges and decongestants from 30 November 2020 to 21 February 2021, was about a half of the sale a year earlier. Public Health England reported no cases of flu in the year 2021 to date, and that there was an 89% rise in sales of Vitamin D to try to boost immunity.
