India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, for a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions.
| States and union territories of India ordered by |
|---|
|
|
|
History[edit]
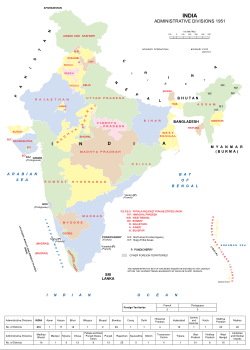
Administrative divisions of India in 1951
Pre-independence[edit]
The Indian subcontinent has been ruled by many different ethnic groups throughout its history, each instituting their own policies of administrative division in the region.[2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12][excessive citations] During the British Raj, the preceding Mughal administrative structure was mostly kept. India was divided into provinces (also called Presidencies) that were directly governed by the British and princely states which were nominally controlled by a local prince or raja loyal to the British Empire, which held de facto sovereignty (suzerainty) over the princely states.
1947–1950[edit]
Between 1947 and 1950 the territories of the princely states were politically integrated into the Indian Union. Most were merged into existing provinces; others were organised into new provinces, such as Rajasthan, Himachal Pradesh, Madhya Bharat, and Vindhya Pradesh, made up of multiple princely states; a few, including Mysore, Hyderabad, Bhopal, and Bilaspur, became separate provinces. The new Constitution of India, which came into force on 26 January 1950, made India a sovereign democratic republic. The new republic was also declared to be a “Union of States”.[13] The constitution of 1950 distinguished between three main types of states:[citation needed]
- Part A states, which were the former governors’ provinces of British India, were ruled by an elected governor and state legislature. The nine Part A states were Assam (formerly Assam Province), Bihar (formerly Bihar Province), Bombay (formerly Bombay Province), East Punjab (formerly Punjab Province), Madhya Pradesh (formerly the Central Provinces and Berar), Madras (formerly Madras Province), Orissa (formerly Orissa Province), Uttar Pradesh (formerly the United Provinces), and West Bengal (formerly Bengal Province).
- The eight Part B states were former princely states or groups of princely states, governed by a rajpramukh, who was usually the ruler of a constituent state, and an elected legislature. The rajpramukh was appointed by the President of India. The Part B states were Hyderabad (formerly Hyderabad Princely State), Jammu and Kashmir (formerly Jammu and Kashmir Princely State), Madhya Bharat (formerly Central India Agency), Mysore (formerly Mysore Princely State), Patiala and East Punjab States Union (PEPSU), Rajasthan (formerly Rajputana Agency), Saurashtra (formerly Baroda, Western India and Gujarat States Agency), and Travancore-Cochin (formerly Travancore Princely State and Cochin Princely State).
- The ten Part C states included both the former chief commissioners’ provinces and some princely states, and each was governed by a chief commissioner appointed by the President of India. The Part C states were Ajmer (formerly Ajmer-Merwara Province), Bhopal (formerly Bhopal Princely State), Bilaspur (formerly Bilaspur Princely State), Coorg State (formerly Coorg Province), Delhi, Himachal Pradesh, Kutch (formerly Cutch Princely State), Manipur (formerly Manipur Princely State), Tripura (formerly Tripura Princely State), and Vindhya Pradesh (formerly Central India Agency).
- The only Part D state was the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, which were administered by a lieutenant governor appointed by the union government.
States reorganisation (1951–1956)[edit]
Andhra State was created on 1 October 1953 from the Telugu-speaking northern districts of Madras State.[14]
The French enclave of Chandernagore was transferred to West Bengal in 1954. In the same year Pondicherry, comprising the former French enclaves of Pondichéry, Karikal, Yanaon and Mahé, was transferred to India; this became a union territory in 1962.[15]
Also in 1954, pro-India forces liberated the Portuguese-held enclaves of Dadrá and Nagar Aveli, declaring the short-lived de facto state Free Dadra and Nagar Haveli. In 1961, it was annexed by India as the Union Territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli.[16][17][18][19]
The States Reorganisation Act, 1956 reorganised the states based on linguistic lines resulting in the creation of the new states.[20] As a result of this act, Madras State retained its name with Kanyakumari district added to form Travancore-Cochin. Andhra Pradesh was created with the merger of Andhra State with the Telugu-speaking districts of Hyderabad State in 1956. Kerala was created with the merger of Malabar district and the Kasaragod taluk of South Canara districts of Madras State with Travancore-Cochin. Mysore State was re-organized with the addition of districts of Bellary and South Canara (excluding Kasaragod taluk) and the Kollegal taluk of Coimbatore district from the Madras State, the districts of Belgaum, Bijapur, North Canara and Dharwad from Bombay State, the Kannada-majority districts of Bidar, Raichur and Gulbarga from Hyderabad State and the Coorg State. The Laccadive Islands, Aminidivi Islands and Minicoy Island which were divided between South Canara and Malabar districts of Madras State were united and organised into the union territory of Lakshadweep.
Bombay State was enlarged by the addition of Saurashtra State and Kutch State, the Marathi-speaking districts of Nagpur Division of Madhya Pradesh and Marathwada region of Hyderabad State. Rajasthan and Punjab gained territories from Ajmer State and Patiala and East Punjab States Union respectively and certain territories of Bihar was transferred to West Bengal.
Post-1956[edit]
Bombay State was split into the linguistic states of Gujarat and Maharashtra on 1 May 1960 by the Bombay Reorganisation Act.[21] Former Union Territory of Nagaland achieved statehood on 1 December 1963.[22] The Punjab Reorganisation Act, 1966 resulted in the creation of Haryana on 1 November and the transfer of the northern districts of Punjab to Himachal Pradesh.[23] The act also designated Chandigarh as a union territory and the shared capital of Punjab and Haryana.[24][25]
Madras State was renamed Tamil Nadu in 1969. North-eastern states of Manipur, Meghalaya and Tripura were formed on 21 January 1972.[26] Mysore State was renamed as Karnataka in 1973. On 16 May 1975, Sikkim became the 22nd state of the Indian Union and the state’s monarchy was abolished.[27] In 1987, Arunachal Pradesh and Mizoram became states on 20 February, followed by Goa on 30 May, while erstwhile union territory of Goa, Daman and Diu’s northern exclaves Damão and Diu became separate union territory as Daman and Diu.[28]
In November 2000, three new states were created; namely, Chhattisgarh from eastern Madhya Pradesh, Uttaranchal from northwest Uttar Pradesh (renamed Uttarakhand in 2007) and Jharkhand from southern districts of Bihar with the enforcement of Madhya Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2000, Uttar Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2000 and Bihar Reorganisation Act, 2000 respectively.[29][30][31][32] Pondicherry was renamed as Puducherry in 2007 and Orissa was renamed as Odisha in 2011. Telangana was created on 2 June 2014 as ten former districts of north-western Andhra Pradesh.[33][34]
In August 2019, the Parliament of India passed the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act, 2019, which contains provisions to reorganise the state of Jammu and Kashmir into two union territories; Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh, effective from 31 October 2019.[35] Later that year in November, the Government of India introduced legislation to merge the union territories of Daman and Diu and Dadra and Nagar Haveli into a single union territory to be known as Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, effective from 26 January 2020.[36][37][38]
Current proposals[edit]
States and Union territories[edit]
States[edit]
| State | ISO 3166-2:IN | Vehicle code |
Zone | Capital | Largest city | Statehood | Population (census 2011)[citation needed] |
Area (km2) |
Official languages[39] |
Additional official languages[39] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andhra Pradesh | IN-AP | AP | Southern | Visakhapatnam (Administrative)[40] Amaravati (Legislative)[40] Kurnool (Judicial)[40] |
Visakhapatnam | 1 November 1956 | 49,506,799 | 160,205 | Telugu | — |
| Arunachal Pradesh | IN-AR | AR | North-Eastern | Itanagar | 20 February 1987 | 1,383,727 | 83,743 | English | — | |
| Assam | IN-AS | AS | North-Eastern | Dispur | Guwahati | 26 January 1950 | 31,205,576 | 78,550 | Assamese | Bengali, Bodo |
| Bihar | IN-BR | BR | Eastern | Patna | 26 January 1950 | 104,099,452 | 94,163 | Hindi | Urdu | |
| Chhattisgarh | IN-CT | CG | Central | Nava Raipur | Raipur | 1 November 2000 | 25,545,198 | 135,194 | Hindi | Chhattisgarhi |
| Goa | IN-GA | GA | Western | Panaji | Vasco da Gama | 30 May 1987 | 1,458,545 | 3,702 | Konkani | Marathi |
| Gujarat | IN-GJ | GJ | Western | Gandhinagar | Ahmedabad | 1 May 1960 | 60,439,692 | 196,024 | Gujarati | — |
| Haryana | IN-HR | HR | Northern | Chandigarh | Faridabad | 1 November 1966 | 25,351,462 | 44,212 | Hindi | Punjabi[41][42] |
| Himachal Pradesh | IN-HP | HP | Northern | Shimla (Summer) Dharamshala (Winter)[43] |
Shimla | 25 January 1971 | 6,864,602 | 55,673 | Hindi | Sanskrit[44] |
| Jharkhand | IN-JH | JH | Eastern | Ranchi | Jamshedpur | 15 November 2000 | 32,988,134 | 74,677 | Hindi | Angika, Bengali, Bhojpuri, Ho, Kharia, Khortha, Kurmali, Kurukh, Magahi, Maithili, Mundari, Nagpuri, Odia, Santali, Urdu[45] |
| Karnataka | IN-KA | KA | Southern | Bengaluru | 1 November 1956 | 61,095,297 | 191,791 | Kannada | — | |
| Kerala | IN-KL | KL | Southern | Thiruvananthapuram | Kochi | 1 November 1956 | 33,406,061 | 38,863 | Malayalam | — |
| Madhya Pradesh | IN-MP | MP | Central | Bhopal | Indore | 26 January 1950 | 72,626,809 | 308,252 | Hindi | — |
| Maharashtra | IN-MH | MH | Western | Mumbai (Summer) Nagpur (Winter)[46] |
Mumbai | 1 May 1960 | 112,374,333 | 307,713 | Marathi | — |
| Manipur | IN-MN | MN | North-Eastern | Imphal | 21 January 1972 | 2,855,794 | 22,347 | Meitei | English | |
| Meghalaya | IN-ML | ML | North-Eastern | Shillong | 21 January 1972 | 2,966,889 | 22,720 | English | Khasi[a] | |
| Mizoram | IN-MZ | MZ | North-Eastern | Aizawl | 20 February 1987 | 1,097,206 | 21,081 | English, Hindi, Mizo | — | |
| Nagaland | IN-NL | NL | North-Eastern | Kohima | Dimapur | 1 December 1963 | 1,978,502 | 16,579 | English | — |
| Odisha | IN-OR | OD | Eastern | Bhubaneswar | 26 January 1950 | 41,974,218 | 155,820 | Odia | — | |
| Punjab | IN-PB | PB | Northern | Chandigarh | Ludhiana | 1 November 1966 | 27,743,338 | 50,362 | Punjabi | — |
| Rajasthan | IN-RJ | RJ | Northern | Jaipur | 26 January 1950 | 68,548,437 | 342,269 | Hindi | English | |
| Sikkim | IN-SK | SK | North-Eastern | Gangtok | 16 May 1975 | 610,577 | 7,096 | English, Nepali | Bhutia, Gurung, Lepcha, Limbu, Manggar, Mukhia, Newari, Rai, Sherpa, Tamang | |
| Tamil Nadu | IN-TN | TN | Southern | Chennai | 1 November 1956 | 72,147,030 | 130,058 | Tamil | English | |
| Telangana | IN-TG | TS | Southern | Hyderabad[b] | 2 June 2014 | 35,193,978[47] | 114,840[47] | Telugu | Urdu[48] | |
| Tripura | IN-TR | TR | North-Eastern | Agartala | 21 January 1972 | 3,673,917 | 10,492 | Bengali, English, Kokborok | — | |
| Uttar Pradesh | IN-UP | UP | Central | Lucknow | Kanpur | 26 January 1950 | 199,812,341 | 243,286 | Hindi | Urdu |
| Uttarakhand | IN-UT | UK | Central | Gairsain (Summer) Dehradun (Winter)[49] |
Dehradun | 9 November 2000 | 10,086,292 | 53,483 | Hindi | Sanskrit[50] |
| West Bengal | IN-WB | WB | Eastern | Kolkata | 26 January 1950 | 91,276,115 | 88,752 | Bengali, Nepali[c] | Hindi, Odia, Punjabi, Santali, Urdu | |
Union territories[edit]
| Union territory | ISO 3166-2:IN | Vehicle code |
Zone | Capital | Largest city | UT established | Population | Area (km2) |
Official languages |
Additional official languages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andaman and Nicobar Islands | IN-AN | AN | Southern | Port Blair | 1 November 1956 | 380,581 | 8,249 | Hindi | English | |
| Chandigarh | IN-CH | CH | Northern | Chandigarh | — | 1 November 1966 | 1,055,450 | 114 | English | — |
| Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu | IN-DH | DD | Western | Daman | 26 January 2020 | 586,956 | 603 | Gujarati, Hindi | Konkani, Marathi | |
| Delhi | IN-DL | DL | Northern | New Delhi | — | 1 November 1956 | 16,787,941 | 1,490 | Hindi | Punjabi, Urdu[51] |
| Jammu and Kashmir | IN-JK | JK | Northern | Srinagar (Summer) Jammu (Winter) |
Srinagar | 31 October 2019 | 12,258,433 | 55,538 | Hindi, Urdu | Dogri, Kashmiri |
| Ladakh | IN-LA | LA | Northern | Leh (Summer) Kargil (Winter)[52] |
Leh | 31 October 2019 | 290,492 | 174,852 | Hindi, English | |
| Lakshadweep | IN-LD | LD | Southern | Kavaratti | 1 November 1956 | 64,473 | 32 | Malayalam, English | — | |
| Puducherry | IN-PY | PY | Southern | Puducherry | 16 August 1962 | 1,247,953 | 492 | French [53] Tamil, English | Malayalam, Telugu | |
Autonomous areas[edit]
The Sixth Schedule of the Constitution of India allows for the formation of autonomous councils to administer areas which have been given autonomy within their respective states.[54] Most of these autonomous areas are located in Northeast India.
Former states[edit]
| Map | State | Capital | Years | Present-day state(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
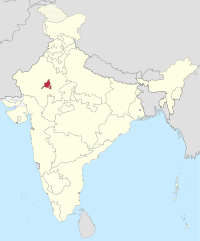 |
Ajmer State | Ajmer | 1950–1956 | Rajasthan |
 |
Andhra State | Kurnool | 1953–1956 | Andhra Pradesh |
 |
Bhopal State | Bhopal | 1949–1956 | Madhya Pradesh |
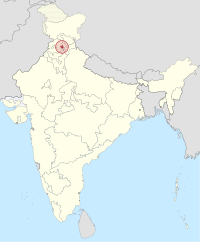 |
Bilaspur State | Bilaspur | 1950–1954 | Himachal Pradesh |
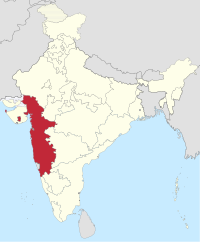 |
Bombay State | Bombay | 1950–1960 | Maharashtra and Gujarat |
 |
Coorg State | Madikeri | 1950–1956 | Karnataka |
 |
East Punjab | Shimla (1947–1953) Chandigarh (1953–1966) |
1947–1966 | Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh and Chandigarh UT |
 |
Hyderabad State | Hyderabad | 1948–1956 | Telangana, and partially Maharashtra and Karnataka |
 |
Jammu and Kashmir | Srinagar (Summer) Jammu (Winter) |
1954–2019 | Jammu and Kashmir UT andLadakh UT |
 |
Kutch State | Bhuj | 1947–1956 | Gujarat |
 |
Madhya Bharat | Indore (Summer) Gwalior (Winter) |
1948–1956 | Madhya Pradesh |
 |
Madras State | Madras | 1950–1969 | Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and partially Karnataka and Kerala |
 |
Mysore State | Mysore | 1947–1973 | Karnataka |
 |
Patiala and East Punjab States Union | Patiala | 1948–1956 | Punjab and Haryana |
 |
Saurashtra | Rajkot | 1948–1956 | Gujarat |
 |
Travancore-Cochin | Trivandrum | 1949–1956 | Kerala and partially Tamil Nadu |
 |
Vindhya Pradesh | Rewa | 1948–1956 | Madhya Pradesh |
Former union territories[edit]
| Map | Name | Zone | Capital | Area | UT established | UT disestablished | Today part of |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Arunachal Pradesh | North-Eastern | Itanagar | 83,743 km2 (32,333 sq mi) | 21 January 1972 | 20 February 1987 | As an Indian state |
 |
Dadra and Nagar Haveli | Western | Silvassa | 491 km2 (190 sq mi) | 11 August 1961 | 26 January 2020 | Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu union territory |
 |
Daman and Diu | Western | Daman | 112 km2 (43 sq mi) | 30 May 1987 | 26 January 2020 | Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu union territory |
 |
Goa, Daman and Diu | Western | Panaji | 3,814 km2 (1,473 sq mi) | 19 December 1961 | 30 May 1987 | Goa state and Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu union territory |
 |
Himachal Pradesh | Northern | Shimla | 55,673 km2 (21,495 sq mi) | 1 November 1956 | 25 January 1971 | As an Indian state |
 |
Manipur | North-Eastern | Imphal | 22,327 km2 (8,621 sq mi) | 1 November 1956 | 21 January 1972 | As an Indian state |
 |
Mizoram | North-Eastern | Aizawl | 21,087 km2 (8,142 sq mi) | 21 January 1972 | 20 February 1987 | As an Indian state |
 |
Nagaland | North-Eastern | Kohima | 16,579 km2 (6,401 sq mi) | 29 November 1957 | 1 December 1963 | As an Indian state |
 |
Tripura | North-Eastern | Agartala | 10,491.65 km2 (4,050.85 sq mi) | 1 November 1956 | 21 January 1972 | As an Indian state |
[edit]
The Constitution of India distributes the sovereign executive and legislative powers exercisable with respect to the territory of any State between the Union and that State.[55]
